Herniated Nucleus Pulposus (HNP)
- General information
- Protrusion of nucleus pulposus (central part of intervertebral disc) into spinal canal causing compression of spinal nerve roots
- Occurs more often in men
- Herniation most commonly occurs at the fourth and fifth intervertebral spaces in the lumbar region
- Predisposing factors include heavy lifting or pulling and trauma
- Medical management
- Conservative treatment
- Bed rest
- Traction
- lumbosacral disc: pelvic traction
- cervical disc: cervical traction
- Drug therapy
- anti-inflammatory agents
- muscle relaxants
- analgesics
- Local application of heat and diathermy
- Corset for lumbosacral disc
- Cervical collar for cervical disc
- Epidural injections of corticosteroids
- Surgery
- Discectomy with or without spinal fusion
- Chemonucleolysis
- injection of chymopapain (derivative of papaya plant) into disc to reduce size and pressure on affected nerve root
- used as alternative to laminectomy in selected cases
- Assessment findings
- Lumbosacral disc
- Back pain radiating across buttock and down leg (along sciatic nerve)
- Weakness of leg and foot on affected side
- Numbness and tingling in toes and foot
- Positive straight-leg raise test: pain on raising leg
- Depressed or absent Achilles reflex
- Muscle spasm in lumbar region
- Cervical disc
- Shoulder pain radiating down arm to hand
- Weakness of affected upper extremity
- Paresthesias and sensory disturbances
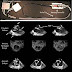
- Diagnostic tests: myelogram localizes site of herniation
- Nursing interventions
- Ensure bed rest on a firm mattress with bed board.
- Assist client in applying pelvic or cervical traction as ordered.
- Maintain proper body alignment.
- Administer medications as ordered.
- Prevent complications of immobility.
- Provide additional comfort measures to relieve pain.
- Provide pre-op care for client receiving chemonucleolysis.
- Administer cimetidine (Tagamet) and diphenhydramine HCl (Benadryl) every 6 hours as ordered to reduce possibility of allergic reaction.
- Possibly administer corticosteroids before procedure.
- Provide post-op care for client receiving chemonucleolysis.
- Observe for anaphylaxis.
- Observe for less serious allergic reaction (e.g., rash, itching, rhinitis, difficulty in breathing).
- Monitor for neurologic deficits (numbness or tingling in extremities or inability to void).
- Provide client teaching and discharge planning concerning
- Back-strengthening exercises as prescribed
- Maintenance of good posture
- Use of proper body mechanics, how to lift heavy objects correctly
- maintain straight spine.
- flex knees and hips while stooping.
- keep load close to body.
- Prescribed medications and side effects
- Proper application of corset or cervical collar
- Weight reduction if needed
Tuesday, May 20, 2008
|
Labels:
musculoskeletal disorder
|
This entry was posted on Tuesday, May 20, 2008
and is filed under
musculoskeletal disorder
.
You can follow any responses to this entry through
the RSS 2.0 feed.
You can leave a response,
or trackback from your own site.
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)






0 comments:
Post a Comment