Angiography
Angiography
: involves introduction of contrast dye into the vascular system to outline the heart and blood vessels
: used to visualize the patency of an artery
Purposes of the Procedure
> Used in the detection of artery stenoses
> Utilized for the detection of congenital anomalies of the coronary circulation, coronary arteriovenous fistulas, and patency of coronary artery bypass grafts
> Used to determine the location, severity, and morphology of stenotic lesions. The resulting information is used to plan either bypass surgery or catheter-based interventions
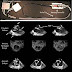
Coronary Angiography Result
Preparation of the Patient:
> Inform the client of the risks involved in this procedure (allergic reaction, embolus, cardiac dysrhythmia).
> Obtain a signed informed consent.
>Ask the patient about allergies to iodine or shellfish
> Determine the location and strength of peripheral pulses.
> Administer mild sedative as ordered before procedure
Procedure:
1. Angiography is performed with the patient awake but sedated. This is usually performed on an outpatient basis, with the patient discharged 4 to 6 hours after the procedure.
2. Placement of the catheter tip into the arteries is carried out under fluoroscopic guidance, and contrast agent is injected by hand during recording of the radiographic image.
Angiography
Post-procedure Care:
> Observe the client for complications.
> Check the injection site for bleeding and inflammation, assessing circulatory status of the extremities, and enforcing bed rest.
> Evaluate client’s response to procedure.
Saturday, August 25, 2007
|
Labels:
angiography,
lab test
|
This entry was posted on Saturday, August 25, 2007
and is filed under
angiography
,
lab test
.
You can follow any responses to this entry through
the RSS 2.0 feed.
You can leave a response,
or trackback from your own site.

0 comments:
Post a Comment